Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric Surgery
Morbid obesity has reached epidemic proportions. Severely obese people have a great difficulty in losing weight. Multiple attempts at losing weight through dietary restriction, exercise and medicines only lead to frustration. In cases of severe obesity, diet, exercise and medicines provide only short-term weight loss and fail to achieve any meaningful weight loss over a long period of time. Most persons regain weight and become more obese in short time. Bariatric Surgery is the standard treatment of morbid or severe obesity. It not only leads to significant and durable weight loss but also in improvement/resolution of diseases associated with obesity.

Who are candidates for bariatric or obesity surgery
Not all obese persons require surgery. The selection is based on calculation of body mass index or BMI. Body mass index or BMI is defined as weight in Kg / height in meters square. For example BMI of a 100 kg man who is 175 cm tall is 32.6. So one should calculate one’s own BMI based on height and weight. Those with BMI > 35 (with or without any diseases) or BMI >30 with one or more of associated diseases especially diabetes and sleep apnea should consult a bariatric surgeon. In Asian/ Indian population Bariatric surgery can be considered if BMI is more than 27.5 along with presence of Type 2 Diabetes mellitus.
Popularity of bariatric surgery can be gauged from the fact that more than 1,40,000 bariatric operations are carried out in United States every year.
What are the side effects or complications after surgery?
Like all surgical procedures, complications can occur after bariatric surgery. However the chances of complications are low. In general the risks of remaining obese are substantially higher than the small risk of surgical complications. Nevertheless, one should be fully aware of all the possible risks before undergoing surgery. Some of the complications can be serious if not detected in time.
Does bariatric surgery lead to nutritional deficiencies?
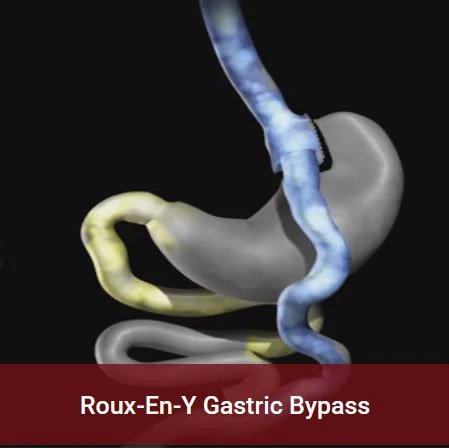
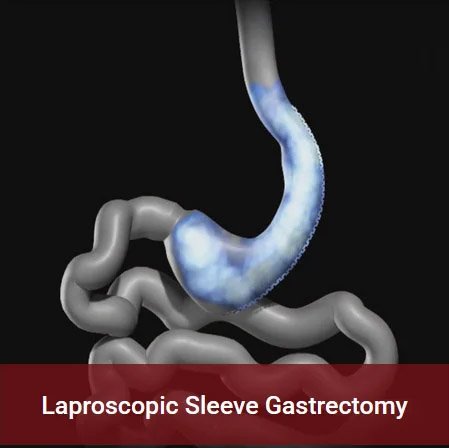
This depends on the type of operation. After sleeve gastrectomy, the chances of developing nutritional deficiencies are low. This problem is commoner after gastric bypass surgery, a procedure in which a part of the food is not absorbed. It is important that one understands the need for postoperative life-long compliance with multivitamins and supplements if one decides for gastric bypass surgery.
To conclude, surgery for morbid obesity is the only method, which provides long-term weight loss. It leads to improvement and often resolution of diseases associated with obesity. Diabetes gets cured in a large number of patients. Surgery has a favourable impact on overall quality of life. The safety is well established. The complication rates are fairly low and acceptable. With proper counselling bariatric surgery leads to a successful outcome in majority.